Definition of Turbocharger:-
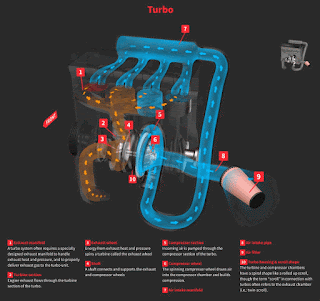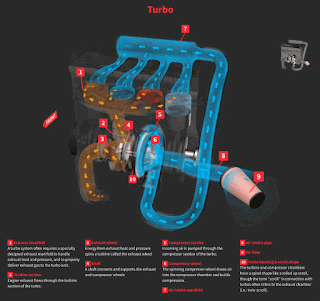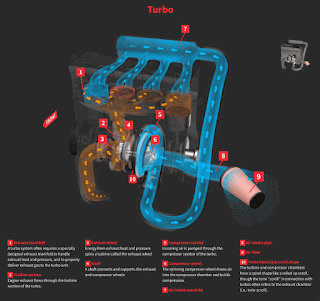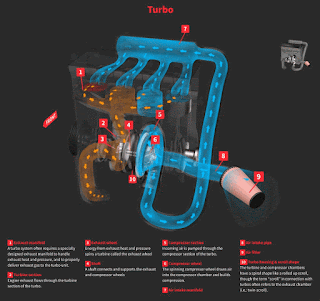
Turbocharger on a car applies a very similar principle to a piston engine. It uses the exhaust gas to drive a turbine. This spins an air compressor that pushes extra air (and oxygen) into the cylinders, allowing them to burn more fuel each second.
Function of Turbocharger:-
A turbo charger is a turbine-driven forced induction device that increases a car engine's efficiency and power output by forcing extra compressed air into the combustion chamber. This improvement over a naturally aspirated engine's power output is due to the fact that the compressor can force more air into the combustion chamber than atmospheric pressure alone.
Turbocharger are extremely common in diesel cars as the turbo aspirated engines can achieve higher compression ratios and consequently deliver more power.
The turbocharger is located the exhaust manifold of the engine. The exhaust from the cylinders spins the turbine, which works like a gas turbine engine. The turbine is connected by a shaft to the compressor, which is located between the air filter and the intake manifold.Turbocharger is a marketing term for fast charger.
A “normal” engine, which is naturally aspirated, simply sucks in the air it can get via the air intake. A turbocharged engine is equipped not only with the regular air intake, but a turbine device that is driven by exhaust gasses which then spins it and forces more air compressed into the engine.
Here are six common turbocharger configurations:-
- Single turbo. The simplest, and still most common, type of turbo is the single-turbocharger set-up.
- Sequential turbos.
- Twin-scroll turbo.
- VGT turbo.
- Variable twin-scroll turbo.
- Electric turbo.
- Significant increase in horsepower.
- Power vs size: allows for smaller engine displacements to produce much more power relative to their size.
- Better fuel economy: smaller engines use less fuel to idle, and have less rotational and reciprocating mass, which improves fuel economy.
- Higher efficiency: turbochargers run off energy that is typically lost in naturally-aspirated and supercharged engines (exhaust gases), thus the recovery of this energy improves the overall efficiency of the engine.
- Turbo Lag. Turbo lag is a problem that is encountered by practically every turbocharger system installed on cars.
- Engine Damage. Improperly installed turbocharger systems have an extremely damaging effect on the engine onto which they are mounted.
- Excessive Heat.
- Turbos reduces the life span of engine.